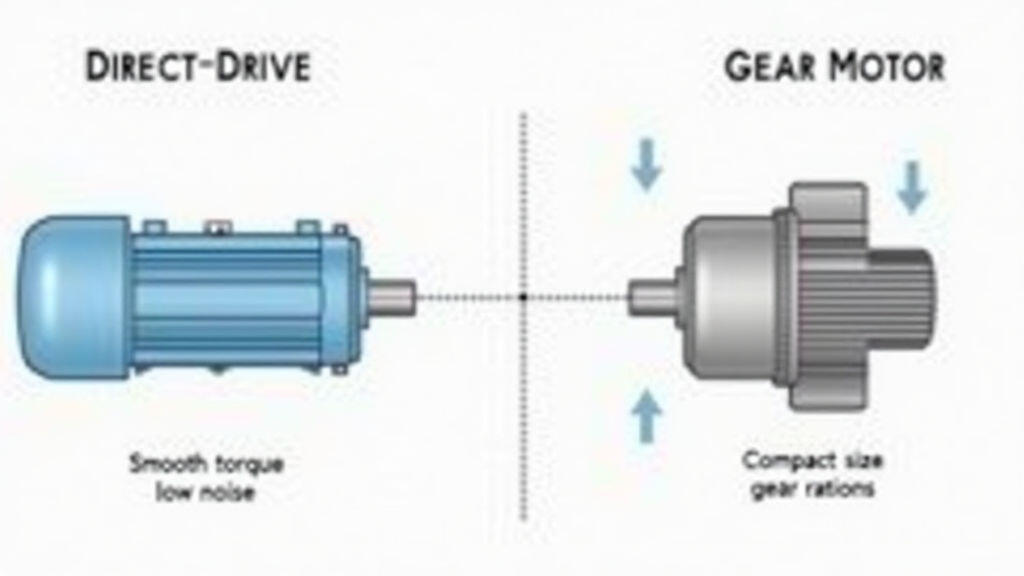
In the fast‑moving world of packaging, the driving forces are speed, precision, reliability, and cost savings. Central to achieving these goals is the selection of the motor that powers the conveyor, cutter, or palletizer. Two families of motors dominate the market today: conventional brushed or brushless DC motors and gear motors. While both can deliver the required torque, recent innovations have created distinct application trends that favor one over the other in specific packaging scenarios.
To appreciate the emerging trends, we first need a clear picture of what each motor type offers.

Manufacturers are increasingly deploying hybrid drive setups that pair a high‑torque gear motor with a micro‑regulator and a short direct‑drive segment. The gear motor brings the high torque needed on the palletizing or priming stage, while the direct‑drive section ensures smooth acceleration and precise speed control during the final packaging closure.
Why this matters: the hybrid system allows packaging lines to handle heavier cartons and maintain near‑zero vibration even at maximum line speed—an important selling point for premium brands that demand both speed and product integrity.
Modern gear motors are being retrofitted with piezoelectric and acoustic sensors that monitor gear tooth stress in real time. When a fault or misalignment is detected, the system can automatically adjust the motor’s input current, or even command a quick maintenance shutdown, thereby preventing catastrophic gear failure.
Benefits:
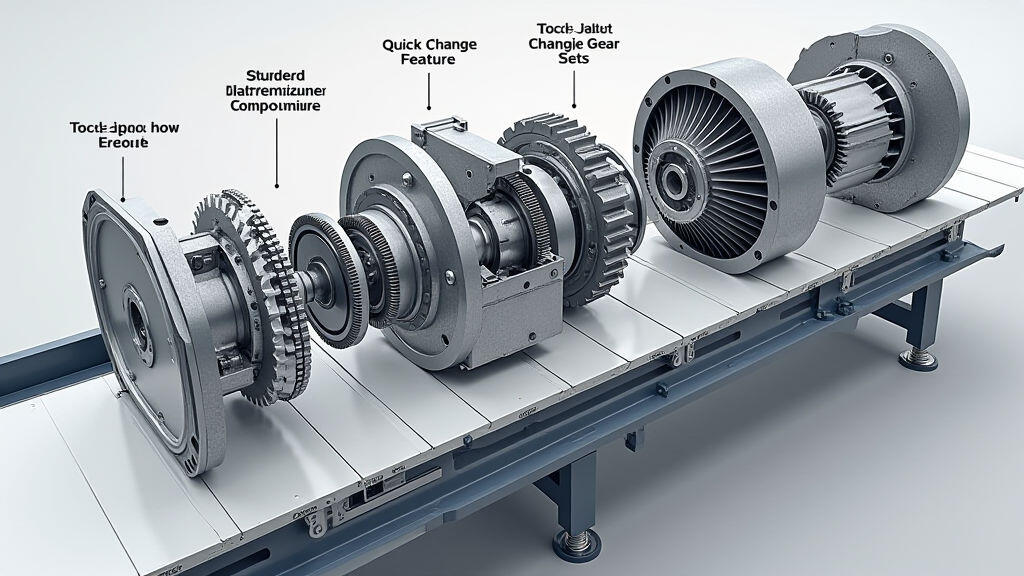
Companies are now treating the gear box as a modular component that can be swapped out to match a new product line or packaging specification. A rapid‑change gear kit allows the same motor head to power a different gear ratio or even switch from a high‑torque gearbox to a high‑speed one within hours, not days.
This trend is especially valuable for seasonal product launches where packaging configurations can vary significantly. Rather than investing in a completely new motor assembly, a simple gear kit configuration change can keep the line operational and reduce the equipment’s total cost of ownership.
A lot of the power loss in gear drives comes from the gear’s internal friction and the motor’s constant speed drives. By pairing a gear motor with an advanced VFD that supplies variable frequency and voltage, the system can operate at just the right speed and torque for each packaging phase, slashing energy consumption by up to 20% in pilot projects.
In high‑speed packaging lines—think powdered or liquid product fillers—the requirement for rapid deceleration and precise thrust is critical. Designers are now creating custom “single‑stage” gearboxes with magnetic couplings that help eliminate backlash and maintain micro‑accurate positioning without the need for an oversized motor.
For regular motors, this level of precision typically demands additional complex gear trains, increasing size and cost. Gear motors provide the needed torque in a condensed form, allowing for tighter layout and faster cycle times.
The packaging industry’s demand for increased speed, precision, and reliability is driving several innovative trends that favor gear motors in specific contexts while retaining a place for direct‑drive regular motors where their strengths shine. Hybrid drive systems blend torque and smoothness, smart sensors extend gear life, modular gear boxes accelerate change, VFD‑driven gear motors slash energy use, and custom high‑speed gearboxes deliver accuracy.
As intelligent manufacturing concepts evolve, the distinction between gear motors and regular motors is no longer one of which is better, but rather where each excels. Embracing these trends ensures packaging lines stay ahead of demand, reduce costs, and maintain the high quality that modern consumers now expect.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked